The food industry is actively seeking new food formulations that can replace and/or mimic animal-based products such as cheese, meat, and eggs due to their evidently environmental and sustainability issues. This trend is combined with the desire to improve the nutritional values of food products aiming to enhance human health. These attempts have led to increased interest in food architecture design and development, which can be illustrated by the significant increase in food innovation entrepreneurships and investment.
The research focuses on the use of various structuring approaches aiming to formulate new food products with unique nutritional and textural attributes. More specifically, the use of oil and water structuring approaches using proteins, polysaccharides, and low molecular weight oil gelators to form bigel system will be presented. The effect of various preparation conditions on the stability and hardness where a significant impact was related to the structuring agent concentration and the homogenization time. Bigel structural, thermal and rheological properties was examined using different emulsifiers with different HLB value in order to evaluate the role of each component on the final gel functionality. The results demonstrate the importance of the interface content in O/W bigel systems, providing an effective way to alter and control the bigel’s bulk properties. This type of systems can potentially enrich the nutritional profile of high saturated fat materials while maintaining desirable textural attributes aiming to improve consumer experience, health and wellbeing.
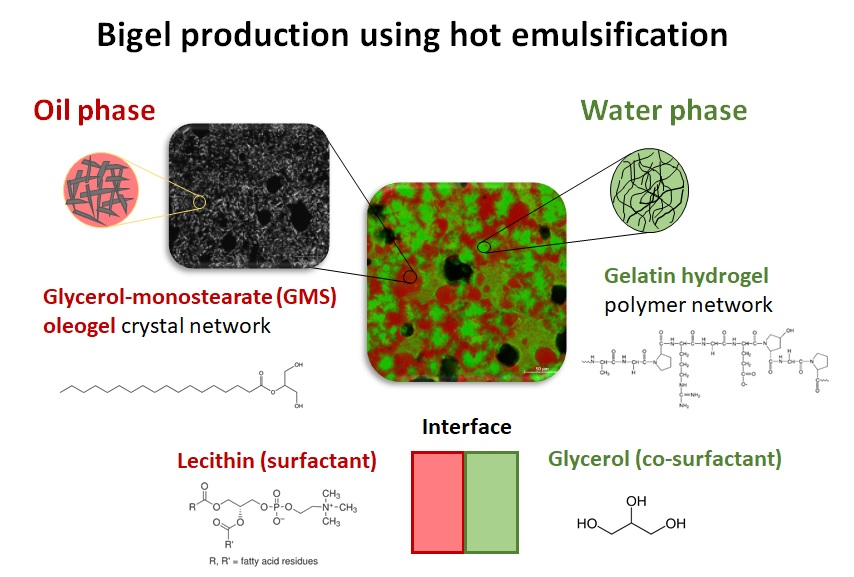
- Tias Samui, Daniel Goldenisky, Jasmine Rosen-Kligvasser, Maya Davidovich-Pinhas “The development and characterization of novel in-situ bigel formulation” Food Hydrocolloids, 113, 106416 (2021).
- Daniel Golodnizky and Maya Davidovich-Pinhas “The effect of the HLB value of sucrose ester on physiochemical properties of bigel systems” Foods, 9(12), 1857 (2020).